ARC Audio is known across the aftermarket motorcycle industry for having introduced some of the first audio upgrade packages specifically for Harley-Davidsons. The MOTO720 is the company’s second generation of extreme-power, motorcycle-specific amplifiers. With four channels of amplification and all the system configuration tools your installer will ever need, this amp should be at the top of your list for upgrades to the audio system in your Harley (or any other brand of motorcycle).
ARC Audio MOTO720 Features
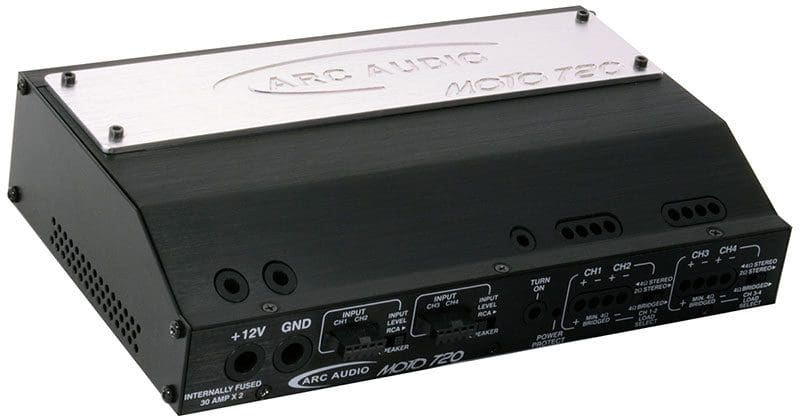
The MOTO720 is based on an aluminum extrusion and measures in at a compact 8.125 inches wide, 5.43 inches deep and 1.8 inch high. The leading edge of the top of the amp is angled so that it will fit inside the fairing of 2014 and newer Harley-Davidson touring motorcycles like the Road Glide and Road King. Wisely, ARC put the connections for the amp on this narrow leading edge so that they won’t interfere with the instrument cluster in the dash. All of the crossover and sensitivity controls are located on the top of the amp under an easily removable machined aluminum cover that bears the ARC Audio logo and the amp model number.

ARC Audio rates the amp as being capable of producing 150 watts per channel into 4-ohm loads, 180 watts per channel into a 2-ohm load, and an impressive 360 watts per channel pair when bridged to a single 4-ohm driver. Unlike many other products and brands out there, ARC’s power rating showcases its output abilities at a continuous power rating at .05% THD, giving you a real-life power rating and not just a number that looks good on paper with marketing attached. More impressive than the robust power ratings is its efficiency. The engineering team at ARC was able to wring out a mind-blowing 94% total efficiency at full power. That’s 10 to 15% better than most competing products. Making the most of the limited electrical systems on a motorcycle is crucial to being able to listen at high-volume levels. With this level of efficiency, the MOTO720 will play louder and longer than its competitors.
Amplifier Connections and Controls
The front edge of the amp includes a custom-tooled terminal block that will accept 8-AWG power and ground connections. Two blocks that will accept 12-AWG speaker cables are at the other end of the amp. The set screws for all 10 terminals plus the remote turn-on connection are accessible through openings in the top cover and are sealed to the inside of the amplifier. Should water get into the screw openings, it will pass through the terminal with no chance of collection and damage. Signal inputs are handled by two five-pin quick-connect jacks. ARC Audio has used these locking jacks as the speaker-level inputs on amps for decades. The amp includes a set of RCA jacks on pigtails for use with aftermarket source units, or it can be connected to the wiring from one of ARC’s Harley-specific wiring kits like the HD-FH2014. A third option is to connect the output of the ARC Audio PSM digital signal processor directly to the amp. As with all new ARC Audio products, the inputs feature a balanced differential design to help eliminate the potential for unwanted noise in the system.
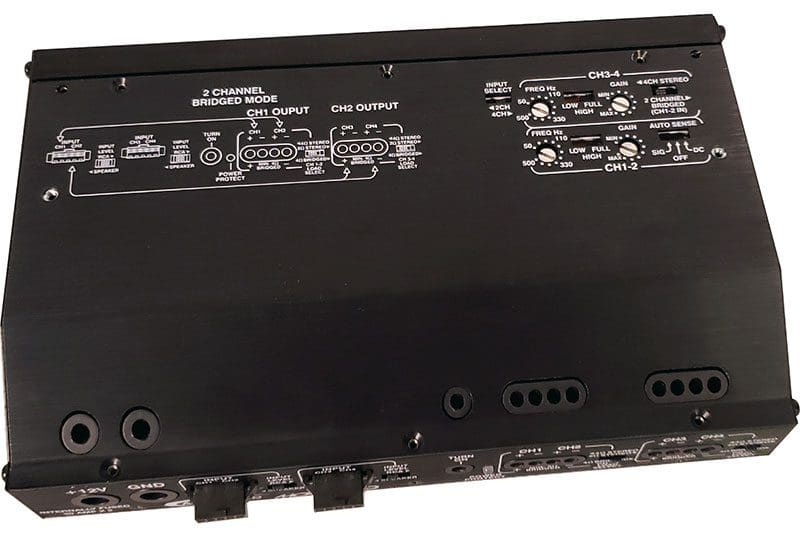

In terms of integrating this amp with the factory source unit on a motorcycle or in any kind of vehicle, ARC has included both DC-Offset and signal-detect remote turn-on features. The sensitivity controls are adjustable from 200 mV to 3.5 V. Each pair of channels has a selectable high- or low-pass crossover that can be set anywhere between 50 and 500 Hz. Additionally, all four channels can be fed using a single pair of inputs based on the position of the Input Select switch. ARC also included a two-channel mode switch that feeds the signal from channel 1 to outputs 1 and 2, and input 2 to channel 3 and 4 for high-power applications. Be careful: 320 watts to a single driver, other than a subwoofer, is a potentially dangerous amount of power.
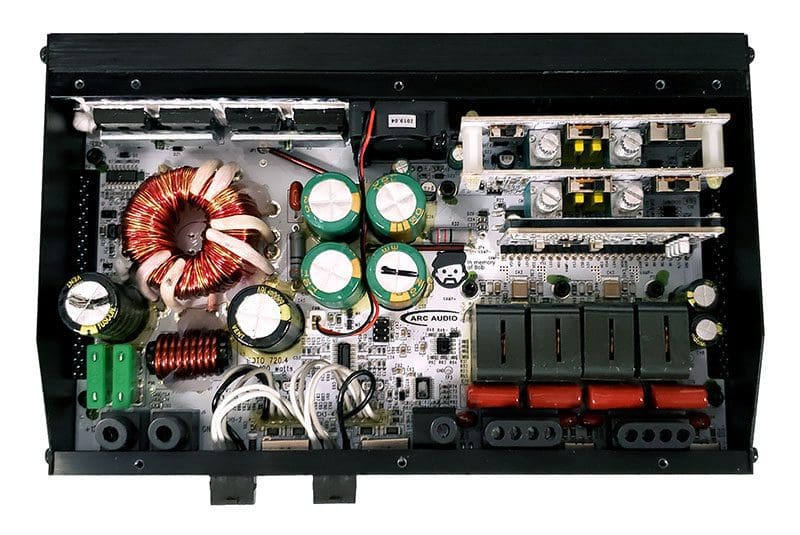
A look inside the amp reveals a tidy and thoughtful design. All the power supply components are kept to the left side of the amp, the input and signal processing components are in the center and on two vertical boards in the back right. You can see the enclosed output chokes on the bottom right. This style of inductor emits less RF noise than typical open designs.
Worth noting is the tribute ARC included inside this amplifier, with a personalized logo in the center of the amp circuit board. It’s a caricature of Bob Morrow. Bob was the ARC Audio representative in the Arizona region and one of the first fields reps to work for the company. He passed away in May 2017. Bob was a true audio enthusiast and loved riding his Gold Wing.

Premium Audio Quality for Motorcycle and Powersports Applications
If you’ve ever had the chance to audition an ARC Audio amplifier, then you’ll understand why they are considered among the best in the industry in terms of sound quality. Drop by your local authorized ARC Audio dealer to check out MOTO720 and the rest of the motorcycle and powersports solutions that are available. You can learn more about ARC Audio products by visiting their website, their Facebook page, their Instagram and their YouTube channel.
This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.